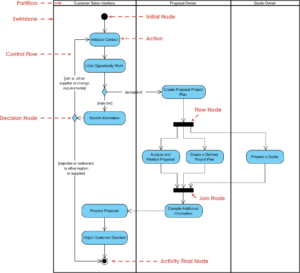
Introduction
This case study explores a business process modeled using Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN). The example depicts a nomination process for an award, illustrating how BPMN can effectively communicate and optimize business workflows. We will interpret each component of the diagram, explain its significance, and provide guidance on using BPMN for similar business process modeling.
Background
The nomination process for awards is a critical activity for organizations that aim to recognize outstanding contributions from individuals or teams. However, this process often faces challenges that can lead to inefficiencies, miscommunication, and delays. The attached BPMN diagram illustrates the current nomination process, highlighting key activities, participants, and decision points.
Current Challenges
- Incomplete Submissions:
- Nominators frequently submit incomplete nomination forms, resulting in delays as judges must request additional information. This back-and-forth communication can slow down the review process.
- Lack of Clarity in Roles:
- Participants in the process may not have a clear understanding of their responsibilities, leading to confusion and potential overlaps in tasks. This lack of clarity can cause delays in the evaluation and decision-making stages.
- Inefficient Review Process:
- The current review process may lack structure, making it difficult for judges to evaluate nominations consistently. Without standardized criteria, evaluations can be subjective and vary significantly between judges.
- Communication Gaps:
- There may be insufficient communication between nominators, judges, and other stakeholders, leading to misunderstandings about the status of nominations and the overall timeline for the process.
- Time Constraints:
- The time taken from nomination submission to announcement of results can be lengthy, leading to frustration among nominators and nominees. A streamlined process is needed to enhance responsiveness.
Goals
To address these challenges, the organization seeks to:
- Streamline the nomination process to minimize delays caused by incomplete submissions and unnecessary communication.
- Clarify roles and responsibilities for all participants to ensure accountability and efficient task execution.
- Standardize evaluation criteria to make the review process more objective and consistent.
- Enhance communication channels to keep all stakeholders informed about the status of nominations and any required actions.
- Reduce the overall timeframe from submission to announcement, ensuring a more responsive and engaging experience for all involved.
Using BPMN for Business Process Modeling
Steps to Model a Business Process with BPMN
- Identify the Process:
- Determine the business process you want to model. Clearly define the objective and scope of the process.
- Define Participants:
- Identify all stakeholders involved in the process. Create pools and lanes to represent different roles and responsibilities.
- Map Activities:
- Break down the process into individual activities. Use rectangles to represent tasks and label them clearly.
- Establish Events:
- Define start and end events for the process. Identify any intermediate events that may affect the flow.
- Incorporate Gateways:
- Identify decision points and use gateways to illustrate different paths based on conditions or events.
- Add Artifacts:
- Use data objects to represent documents or information used throughout the process. This addition helps clarify how information flows.
- Review and Refine:
- Review the BPMN diagram with stakeholders to ensure accuracy and clarity. Make adjustments based on feedback to improve understanding.
- Implement and Monitor:
- Once the BPMN diagram is finalized, implement the process in your organization. Monitor its performance and make iterative improvements as necessary.
Overview of the BPMN Diagram
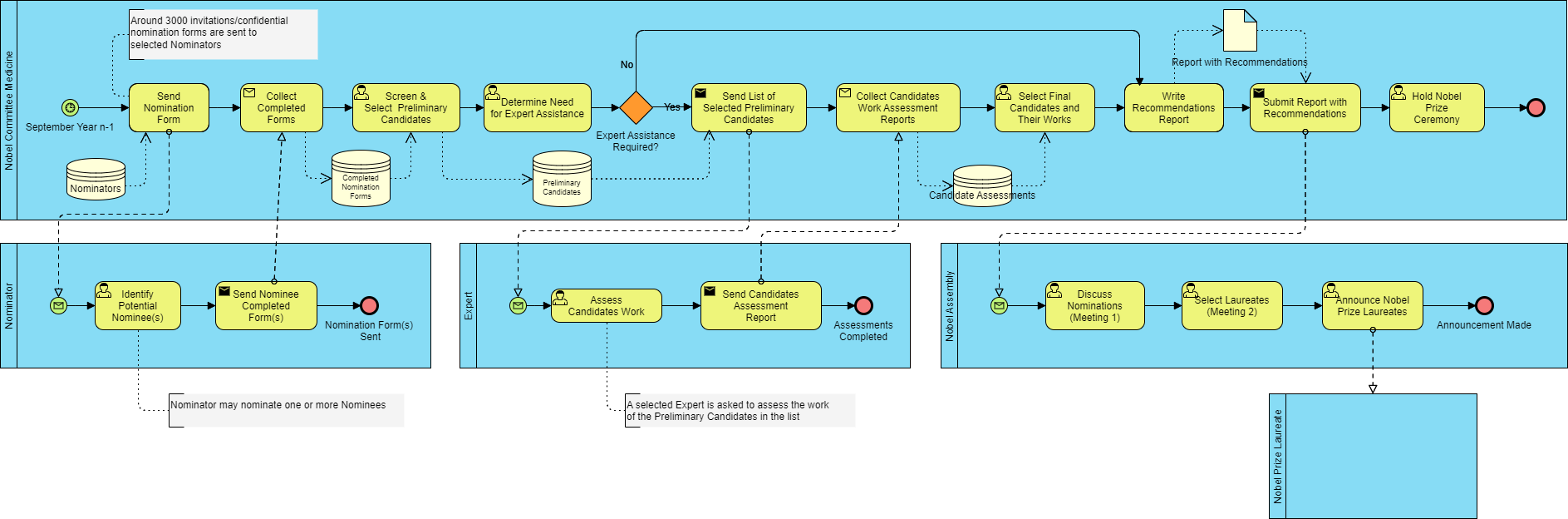
The BPMN diagram represents the following key elements:
- Participants (Pools and Lanes):
- The process involves multiple stakeholders, including Nominees, Nominators, and Judges. Each participant is represented in separate pools or lanes, clarifying roles and responsibilities.
- Activities:
- Key activities in the process include:
- Sending nomination forms.
- Reviewing completed forms.
- Discussing and evaluating nominations.
- Finalizing and announcing award results.
- Key activities in the process include:
- Events:
- Events trigger various activities:
- Start events initiate the process when a nomination is submitted.
- End events signify the completion of the process when results are announced.
- Events trigger various activities:
- Gateways:
- Decision points determine the flow of the process, such as whether nominations are complete or require further information.
- Artifacts:
- Data objects represent documents like nomination forms and reports that are crucial for the process.
Interpretation of the BPMN Diagram
Step-by-Step Breakdown
- Initiation:
- The process begins when nominators send nomination forms. This is denoted by a start event, indicating the commencement of the workflow.
- Nominee Identification:
- Nominators identify potential nominees and complete the nomination forms. This activity is essential for gathering the necessary information for evaluation.
- Review Process:
- Once forms are submitted, judges review them. This includes checking for completeness and eligibility. If forms are incomplete, a decision gateway directs the judges to request additional information.
- Discussion and Evaluation:
- Judges discuss the nominations and evaluate the candidates. This collaborative review ensures that all perspectives are considered before making a decision.
- Finalization and Announcement:
- After discussions, judges finalize the results, which are documented in a report. The process concludes with the announcement of award recipients.
Conclusion
BPMN is a powerful tool for visualizing and optimizing business processes. By clearly outlining roles, activities, and decision points, organizations can enhance communication, streamline workflows, and improve overall efficiency. This case study illustrates how to utilize BPMN effectively, serving as a guide for professionals looking to implement business process modeling in their operations.
The case study of the nomination process modeled using BPMN highlights the effectiveness of this standardized notation in visualizing and optimizing business workflows. By mapping out the process, we identified key challenges such as incomplete submissions, lack of role clarity, inefficient reviews, communication gaps, and time constraints.
BPMN provided a clear framework to understand the intricacies of the nomination process, emphasizing the interactions between nominators, judges, and other stakeholders. It facilitated a comprehensive view of the workflow, enabling us to pinpoint areas for improvement.
By implementing the suggested enhancements, such as streamlining submissions, clarifying roles, standardizing evaluation criteria, and enhancing communication, the organization can significantly improve the nomination process. These changes will lead to a more efficient, transparent, and responsive system, ultimately fostering a positive experience for all participants involved.
Overall, this case study illustrates the value of BPMN not only as a modeling tool but also as a catalyst for process improvement, driving better outcomes in business operations. As organizations continue to evolve, leveraging BPMN will remain essential for effective process management and optimization.