Introduction to BPMN
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a graphical representation for specifying business processes in a workflow. It serves as a bridge between business processes and their implementation, ensuring that all stakeholders, from business analysts to technical developers, can understand and work with the models.
Purpose of BPMN
The primary goal of BPMN is to provide a notation that is easily understandable by all business users. It allows for the creation of Business Process Diagrams (BPDs) that visually represent the flow of activities and decisions within a business process. This facilitates better communication and coordination across different levels of an organization.
Levels of BPMN
BPMN can be applied at three different levels:
- Descriptive Process Models: High-level modeling suitable for analysts familiar with flowcharts.
- Analytic Process Models: Incorporate concepts commonly used in BPMN training.
- Executable Process Models: Focus on elements required for executable models.
Evolution of BPMN
BPMN has evolved significantly since its inception by the Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI). The major milestones include:
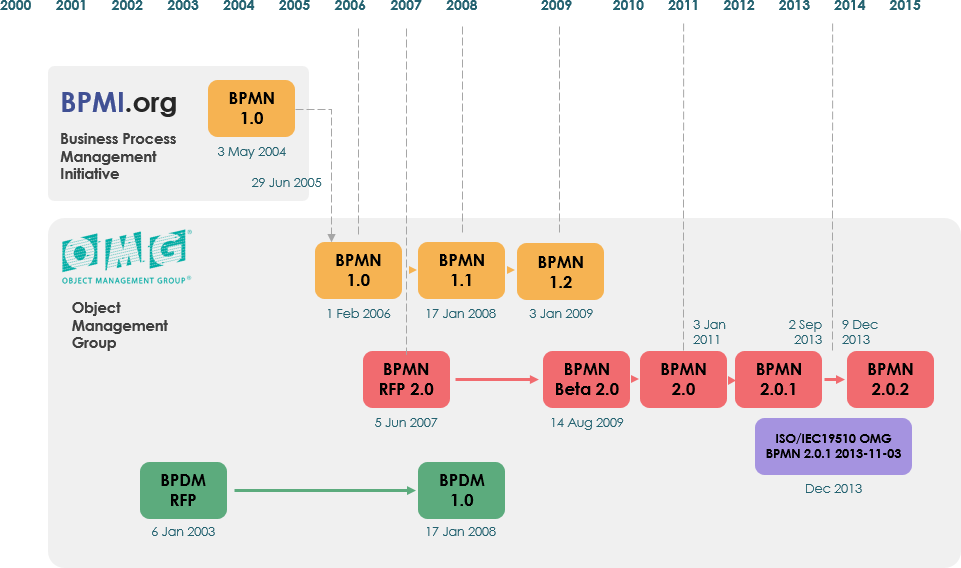
- BPMN 1.0: Released in May 2004.
- BPMN 2.0: Developed in 2010, with the current version (2.0.2) published by ISO in December 2013.
BPMN Core Elements
A BPD consists of several graphical elements categorized into four main groups:
1. Flow Objects
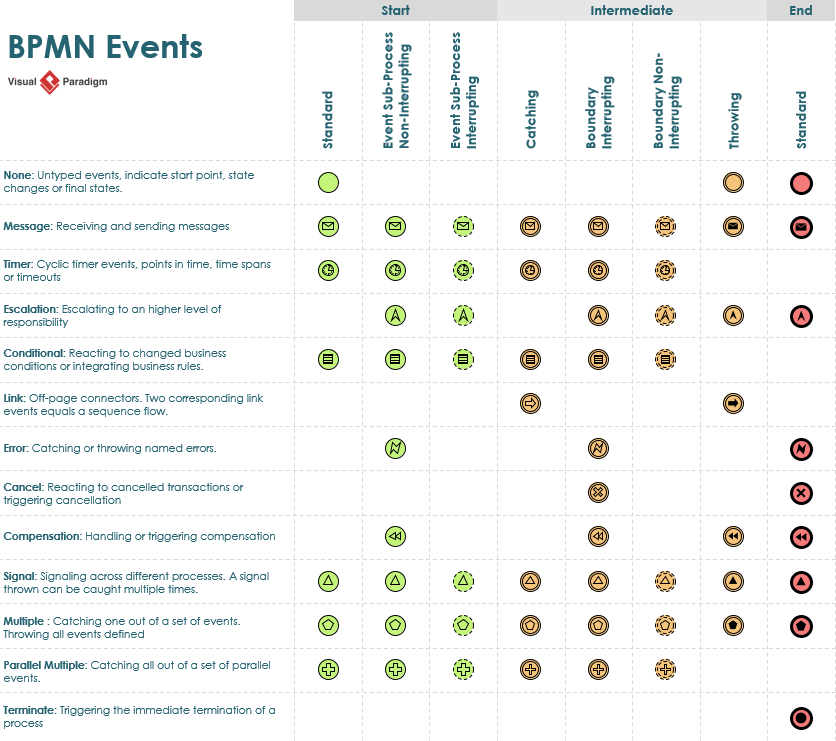
- Event: Represented by a circle, indicating something that happens in the process. Types include:
- Start Event: Marks the beginning of a process.
- Intermediate Event: Occurs between start and end.
- End Event: Indicates the conclusion of a process.
- Activity: Represented by a rounded rectangle, it refers to work performed. Types include:
- Task: A single unit of work.
- Sub-Process: A compound activity, indicated by a plus sign.
- Gateway: Represented by a diamond shape, used to control the flow of the process. Types include:
- Exclusive Gateway: One path is followed.
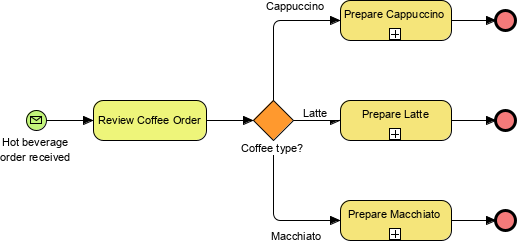
- Inclusive Gateway: One or more paths can be taken.
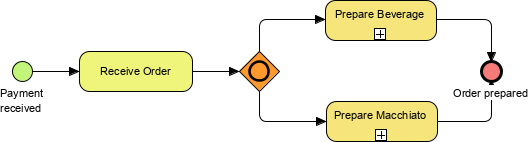
- Parallel Gateway: All paths are followed.
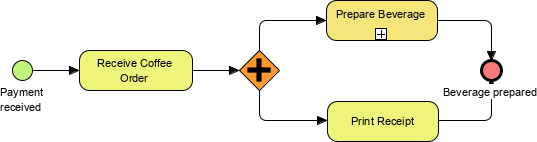
- Inclusive Gateway: One or more paths can be taken.
- Exclusive Gateway: One path is followed.
2. Connecting Objects
Connecting objects link flow objects and provide the structure of the process:

- Sequence Flow: Solid line with an arrowhead, indicating the order of activities.
- Message Flow: Dashed line, showing information flow across organizational boundaries.
- Association: Connects artifacts and provides additional context.
3. Swimlanes
Swimlanes categorize activities based on responsibilities:
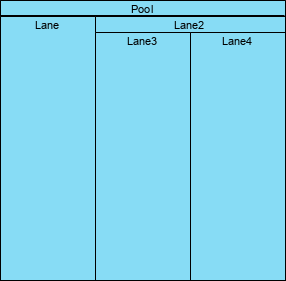
- Pool: Represents a participant in a process, acting as a container for activities.
- Lane: A sub-partition within a pool, organizing and categorizing activities.
4. Artifacts
Artifacts provide additional contextual information about the process:
- Data Object: Shows how data is required or produced.
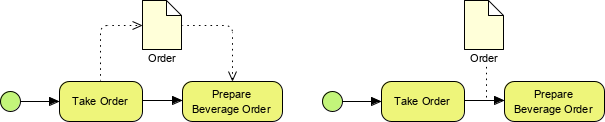
- Data Store: Represents persistent data storage.
- Group: A dashed rectangle for documenting or analyzing purposes.
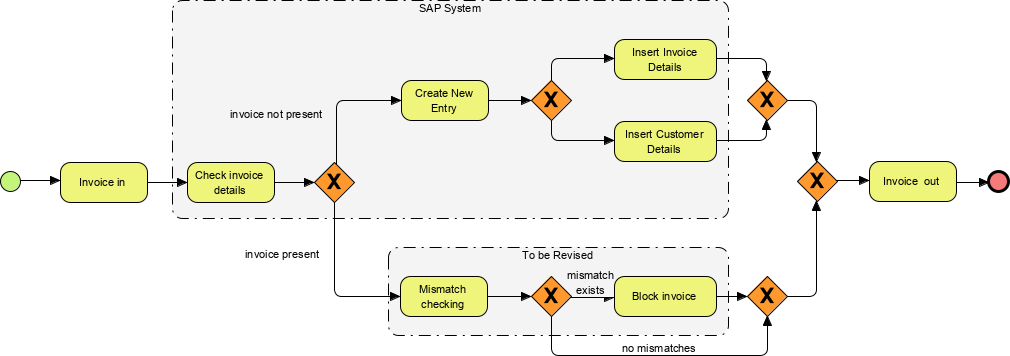
- Annotation: Textual information for explaining elements in the diagram.
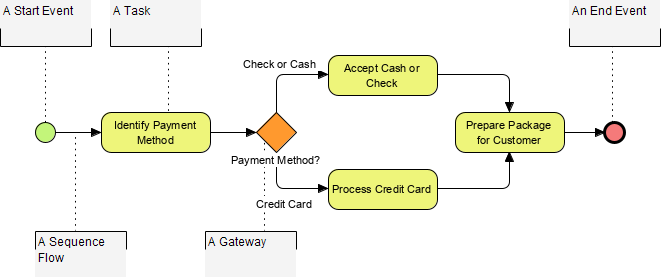
BPMN Notation: Simple or Complex?
BPMN allows for complexity while maintaining a consistent look and feel. For example, events can have variations without altering their basic representation. This adaptability makes BPMN suitable for various modeling situations.
Conclusion
Understanding BPMN notation is essential for effective business process modeling. By utilizing core elements, connecting objects, swimlanes, and artifacts, BPMN provides a comprehensive framework for visualizing and communicating business processes. This promotes clarity and collaboration among all stakeholders, ultimately helping organizations achieve their business goals.
BPMN Learning Resources
Here’s a list of BPMN articles with embedded URLs based on the information provided:
- Best UML & BPMN Tool – Visual Paradigm Modeler
- bpmn | Visual Paradigm User-Contributed Diagrams / Designs
- How to Draw BPMN Conversation Diagram? – Visual Paradigm Tutorials
- How to Create BPMN Diagram? – Visual Paradigm
- Automatically create process diagrams from Excel data (BPMN)
- How to draw an EPC Diagram – Visual Paradigm
- How to draw a Business Concept Diagram – Visual Paradigm
- Visual Paradigm BPMN – Visual Paradigm BPMN site
- Visual Paradigm – UML, Agile, PMBOK, TOGAF, BPMN and More!
- Exporting BPMN 2.0 – Visual Paradigm
- BPMN Archives – Visual Paradigm Blog
- Plantillas de Diagramas de Procesos de Negocio – Visual Paradigm
- BPMN – Pizza Order Process – Visual Paradigm Community Circle
- What is Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD)? – Visual Paradigm
- BPMN Activity Types Explained – Visual Paradigm
- How to Find Use Cases from Business Process (BPMN)? – Visual Paradigm