Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a standardized graphical notation that allows organizations to model their business processes in a clear and understandable way. This article explores how to effectively use BPMN, its benefits, and a step-by-step approach to modeling your business processes.
What is BPMN?
BPMN provides a set of symbols and rules for creating diagrams that represent business processes. These diagrams help stakeholders visualize the workflow, identify inefficiencies, and facilitate communication between different departments. BPMN is widely adopted due to its comprehensiveness and ease of understanding, making it suitable for both technical and non-technical audiences.
Why Use BPMN?
- Clarity and Standardization: BPMN offers a standardized way to represent processes, ensuring that everyone in the organization understands the workflow consistently.
- Improved Communication: By using visual representations, BPMN facilitates better communication among stakeholders, including management, analysts, and operational staff.
- Process Optimization: Modeling processes helps identify bottlenecks, redundancies, and inefficiencies, allowing organizations to streamline operations and improve productivity.
- Documentation: BPMN serves as an excellent documentation tool, helping organizations maintain clear records of their processes, which is useful for training and compliance purposes.
- Integration with Other Systems: BPMN diagrams can be integrated with workflow management systems and business rules engines, supporting automation and enhancing process management.
How to Model a Business Process Using BPMN
Step 1: Define the Process Scope
Start by identifying the process you want to model. Clearly define its boundaries, objectives, and the stakeholders involved. Understand what triggers the process and what the desired outcomes are.
Step 2: Gather Information
Collect detailed information about the steps involved in the process. Engage with stakeholders to gather their insights, observe the current workflow, and document the existing process.
Step 3: Identify Key Elements
Identify the key elements of your process, including:
- Events: Triggers that start or end the process (e.g., receiving a customer order).
- Activities: Tasks or actions performed within the process (e.g., processing the order).
- Gateways: Decision points that determine the flow of the process (e.g., whether to approve a request).
- Flows: Arrows that indicate the sequence of activities.
Step 4: Create the BPMN Diagram
Using BPMN symbols, start creating your diagram:
- Start Event: Represent the beginning of the process.
- Tasks: Use rounded rectangles to represent individual tasks or activities.
- Gateways: Use diamond shapes to indicate decision points.
- End Event: Indicate the conclusion of the process with a circle.
Problem Description for BPMN Example
In a manufacturing company focused on producing custom products, the process of handling client requests is crucial for maintaining efficiency and client satisfaction. The company receives various product requests, which initiate a structured workflow to ensure that all requirements are met before production begins.
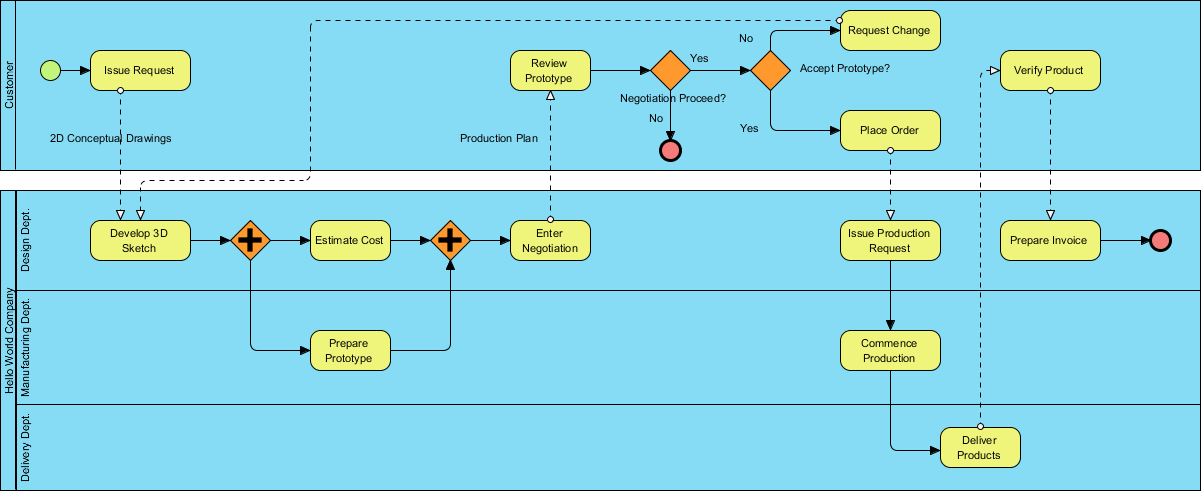
- Initiation of Request: The process starts when a client submits an Issue Request for a new product, accompanied by 2D Conceptual Drawings. This request is received by the design team.
- Development Phase: The design team begins by developing a 3D Sketch of the product. Concurrently, they Estimate Costs associated with production. This step is critical to ensure that the project remains within budget.
- Negotiation Process: After the initial design and cost estimation, the team prepares a Prototype. Once the prototype is ready, it is presented to the client for review. The client has the option to request changes based on their feedback.
- Client Review: If the client accepts the prototype, the process moves forward to Place Order and subsequently to the Issue Production Request. However, if the client requests changes, a Review Prototype phase is initiated, which may lead to further negotiation on design and costs.
- Finalizing Production: Once all negotiations are settled and the prototype is accepted, the team proceeds to Commence Production. Following the completion of production, the company prepares an Invoice to deliver to the client.
- Delivery of Product: The final step involves the Delivery of Product to the client, marking the end of the workflow.
Step 5: Validate the Diagram
Once the diagram is created, validate it with stakeholders to ensure accuracy and completeness. Discuss the flow, decisions, and any potential improvements that can be made.
i.e. Once the BPMN diagram is created, it’s crucial to validate it with stakeholders to ensure accuracy and completeness. Here’s how to do it effectively:
- Review Session: Organize a review session with key stakeholders, including process owners, team members, and any other relevant parties. Present the diagram and walk them through each component.
- Gather Feedback: Encourage participants to provide feedback on the flow of the process. Ask questions like:
- Are there any steps missing?
- Are the decision points accurately represented?
- Do the roles and responsibilities align with actual practices?
- Make Revisions: Based on the feedback, make necessary revisions to the diagram. Ensure that all stakeholders agree with the final version to avoid any misunderstandings later.
Step 6: Analyze and Optimize
Analyze the BPMN diagram to identify areas for improvement. Look for:
- Redundant tasks that can be eliminated.
- Steps that can be automated.
- Decision points that can be streamlined.
i.e. After validating the BPMN diagram, the next step is to analyze it for improvement opportunities:
- Identify Bottlenecks: Look for stages in the process where delays or inefficiencies occur. These might be indicated by complex gateways or numerous tasks that take a long time to complete.
- Evaluate Redundancies: Assess if there are any duplicated tasks or unnecessary steps that can be eliminated to streamline the process.
- Consider Automation: Identify tasks that could be automated through technology. For example, data entry and approval processes are often ripe for automation, which can save time and reduce errors.
- Decision Optimization: Review the gateways in the process. Ensure that decision points are clear and that the criteria for decisions are well-defined to avoid confusion.
- Document Suggested Improvements: Create a list of proposed changes and enhancements alongside the BPMN diagram for future reference.
Step 7: Document and Share
Document the BPMN diagram and any accompanying information. Share it with all relevant stakeholders and ensure that it is accessible for future reference.
i.e. Once analysis and optimization are complete, it’s important to document and share the BPMN diagram effectively:
- Create Comprehensive Documentation: Alongside the BPMN diagram, document additional details such as:
- Objectives of the process
- Roles and responsibilities of involved parties
- Assumptions made during the modeling
- Any constraints or limitations identified during the analysis
- Distribute to Stakeholders: Share the finalized BPMN diagram and accompanying documentation with all relevant stakeholders. Use collaborative platforms, email, or internal knowledge bases to ensure accessibility.
- Training and Awareness: If the process changes significantly, conduct training sessions for affected employees to familiarize them with the new workflow and expectations.
Step 8: Review and Update Regularly
Business processes evolve over time. Regularly review and update your BPMN diagrams to reflect changes in the workflow, technology, or organizational structure.
i.e. Business processes are dynamic and may change over time. Implementing a regular review process is essential:
Modeling business processes using BPMN is an invaluable practice for organizations seeking to enhance clarity, communication, and efficiency within their operations. By adopting a structured approach to BPMN, businesses can create clear visual representations of their workflows, enabling stakeholders to understand and engage with processes more effectively.
The benefits of BPMN extend beyond mere documentation; they facilitate process optimization, help identify inefficiencies, and promote a culture of continuous improvement. Through regular validation, analysis, and updates, organizations can ensure their BPMN diagrams remain relevant and aligned with evolving business goals.
Ultimately, leveraging BPMN empowers organizations to streamline their operations, improve collaboration among teams, and drive better decision-making. Embracing this powerful modeling language not only enhances process management but also positions organizations for sustained success in an increasingly competitive landscape.
- BPMN Modeling Software – Visual Paradigm
- Introduction to BPMN Part I – Visual Paradigm
- Easy-to-Use BPMN Tools – Visual Paradigm
- BPMN – A Comprehensive Guide – Visual Paradigm Guides
- Best UML & BPMN Tool – Visual Paradigm Modeler
- Comprehensive BPMN Diagram Tutorial – Visual Paradigm Blog
- Understanding BPMN: A Comprehensive Overview – Visual Paradigm Guides
- How to Create BPMN Diagram? – Visual Paradigm Tutorials
- Business Process Modeling Using BPMN – Visual Paradigm Guides